Biking Trail
The “Pa Sam Yuk” or “Three eras of Forest” biking trail will take you to observe shadiness and beauty of plant species in Sri Nakhon Khuean Khan Park. You will discover nature-recovery of forest, attempts of human beings in forest rehabilitation, and a way of working in an orchard. These activities will let you enjoy the natural wonders such as Suicide tree scrub, Nipa palm jungle, Mangrove apple tree, big Ironwood tree, an ancient coconut orchard, etc.
The trail surface is 2-km long and covered by asphalt and compacted dirt sections. It requires approximately 45 minutes of biking.
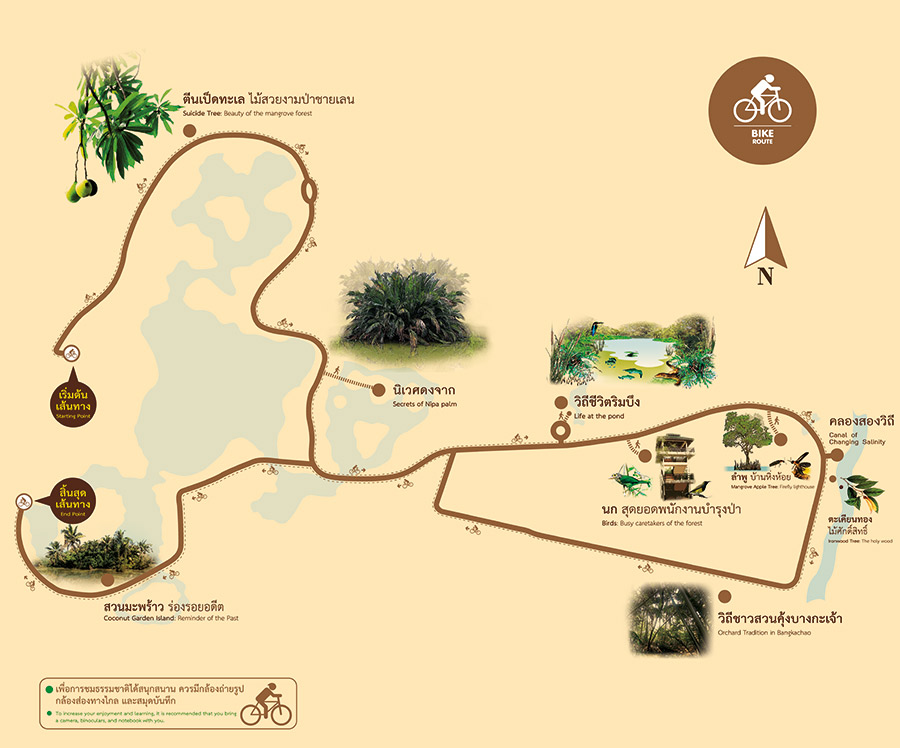
Interesting Point
1) Nipa Palm Grove
The Nipa palm grove in front of us is part of an Estuarine Ecosystem in the area located between a river and a sea. The area is influenced by tides. Plants usually found in an estuarine ecosystem are Mangrove apple trees, Nipa palms, Queen Sago palms and Flagellanria Indica.
In the old days, villagers planted Nipa palms to create wind barriers and to show their rights over the land. It is a very useful tree. Its stalk was used as firewood, new leaves are used to roll cigarettes, old leaves used to be a package for traditional Thai sweets. Thatched roofs and walls are made of very old leaves.
2) The Forest Restoration for Eco-Learning
Sri Nakhon Khuean Khan Park allocates an area of 40-rai for forest ecological restoration study and learning area. The restored ecological forest perfectly replicates the entire ecosystem of Bang Kachao, comprising three types of forests:
- Swamp forest in the marshy area caused by rain
- Mangrove forest located in the river mouth area and affected by tides
- Lowland evergreen forest on the upland area.
3) Life at the Pond
Brackish pond is flooded all year round, so trees and aquatic plants adapted to environment. In addition, this pond is also important to animal’s habitat.
4) Birds: Busy caretakers of the forest
Sri Nakhon Khuean Khan Park is home to almost 100 bird species, accounting for one-tenth of all bird species in Thailand. Birds here are diverse in color and habits and include both resident and migratory species.
5) Mangrove Apple Tree: Fireflies’ home
Mangrove apple trees grow on marshy land and are easily identified by the tapered ‘breathing roots’ which sprout near their base. Fireflies congregated in Mangrove apple trees since the tall and loose shrub helps make the males’ combined flashes brighter and visible from a greater distance and better attract females.
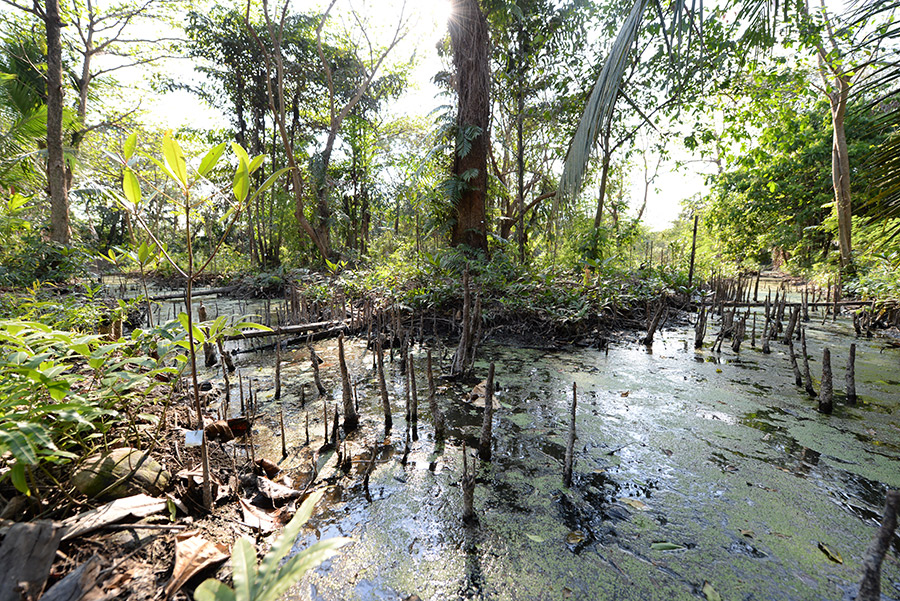
6) Swamp Forest
The fresh water flooded area is located along river bank and the lowland marsh which is flooded during the rainy season and dries during the dry season. The swamp forest in forest ecological restoration study and learning area covers 27 Rais. There are 26 species of plants. The significant plants are, for example, Red sandalwood tree, White cheesewood, Jambolian plum, Kan krao, Mangrove trumpet tree, Luna nut and Ficus.
7) Mangrove Forest in the Brackish Area
The special feature of mangrove forest in the brackish area on the river mouth is that the salinity of the water is not stable throughout the year. Therefore, the plants growing in the area have to adapt to tides and different levels of salinity. The species of plants found here are Mangrove apple trees, Nipa palms, Queen sago palms and Flagellaria indica whereas Rhizophora sp. is the dominant plant in the mangrove forest on the shoreline.
The mangrove forest in forest ecological restoration study and learning area covers 10.55 Rais.

8) Lowland Evergreen Forest
This kind of forest is located on the upland area where it is flooded only in the rainy season. The original plants grown are ones in the Dipterocarpus family such as Ironwood trees, White meranti, and Yang. It covers only 3 Rais of the forest ecological restoration study and learning area.
The additional 15 species of selected plants grown are Ironwood tree, White meranti, Yang, White cheesewood, Ebony tree, Jambolan plum, Kan krao, Mango, Sesban, Mansonia gagei, Champa, Bo tree, Cinnamon, Red sandal wood Tree and Knema erratica.
